A slow WordPress website can frustrate visitors, hurt your SEO rankings, and tank conversions. Studies show that 40% of users abandon a site that takes over 3 seconds to load, and Google prioritizes fast-loading pages in its search results. Whether it’s bloated themes, unoptimized images, or server issues, a sluggish WordPress site can stem from multiple culprits. The good news? You can speed up your WordPress website with practical, actionable steps. In this guide, we’ll first cover how to check your website’s speed and identify what’s slowing it down, then dive into 12 proven ways to improve WordPress load time, boost user experience, and enhance your site’s performance. Let’s get started!
Table of Contents
Why Website Speed Matters
Slow load times lead to higher bounce rates, as impatient users leave before engaging with your content. Google’s algorithm factors in page speed, meaning a slow site could drop in search rankings. For e-commerce sites, even a one-second delay can reduce conversions by 7%. By optimizing your WordPress performance, you create a better experience for users, improve SEO, and drive more sales or engagement.
How to Check Your WordPress Website Speed
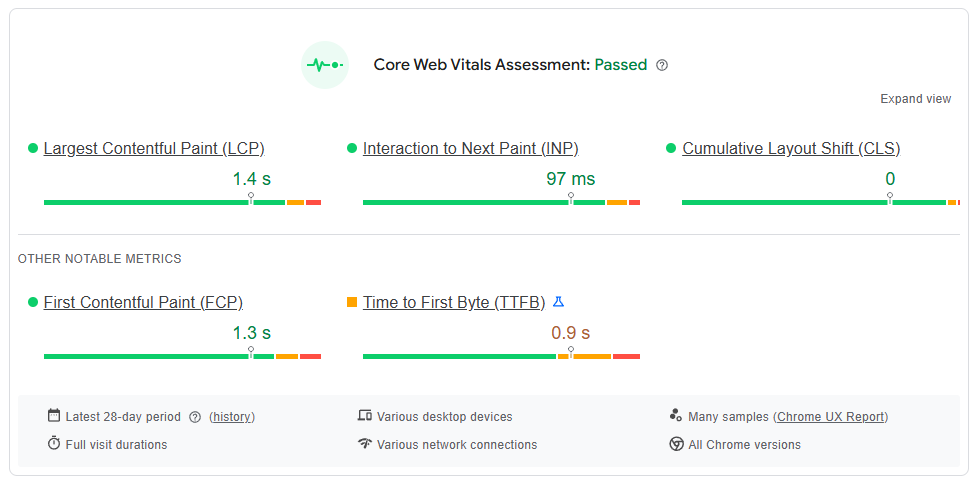
Before diving into fixes, you need to know how fast (or slow) your site is and where the bottlenecks are. Testing your website’s speed provides a baseline and helps you track improvements.
- Tools to Use:
- Google PageSpeed Insights: Analyzes mobile and desktop performance, offering actionable suggestions to improve WordPress load time.
- GTmetrix: Provides detailed reports on load times, waterfall charts, and optimization opportunities.
- Pingdom: Measures speed from multiple global locations, ideal for testing CDN performance.
- How to Test:
- Visit one of the tools above and enter your website URL.
- Run the test and review key metrics like page load time, server response time, and total page size.
- Note specific issues (e.g., large images, slow server response) to prioritize your optimization efforts.
- Best Practices:
- Test your site from multiple locations to understand global performance.
- Run tests at different times to account for server load variations.
- Save reports to compare before and after implementing fixes.
Pro Tip: Aim for a load time under 2 seconds and a server response time below 200ms for optimal performance.
What Slows Down Your WordPress Website?
Understanding the root causes of a slow WordPress site is key to fixing it. Here are the most common culprits:
- Heavy Themes and Plugins: Feature-rich themes or poorly coded plugins add excessive code and database queries, slowing your site.
- Unoptimized Images: Large, uncompressed images increase page size and load times, especially on mobile devices.
- Poor Hosting: Shared or low-quality hosting lacks the resources to handle WordPress efficiently, leading to slow server response times.
- Uncached Pages: Without caching, WordPress generates pages dynamically for each visitor, taxing your server.
- External Scripts: Third-party scripts (e.g., ads, analytics, social widgets) create additional HTTP requests, delaying rendering.
- Bloated Database: Accumulated post revisions, spam comments, and transients slow down database queries.
- Outdated Software: Running old versions of PHP, WordPress, or plugins reduces performance and security.
By addressing these issues, you can significantly reduce page load speed and improve WordPress performance. Let’s explore the solutions!
12 Proven Ways to Speed Up Your WordPress Website

1. Choose a Lightweight WordPress Theme
The Problem: Heavy, feature-packed themes often come with bloated code, excessive scripts, and unnecessary styling that slow down your site. Themes like Avada or Divi, while versatile, can overload your server if not optimized.
The Solution: Opt for a lightweight, performance-focused theme to reduce page load speed. Themes like Astra, GeneratePress, or Neve are designed with speed in mind, offering minimal code and fast load times.
- How to Implement:
- Browse the WordPress theme directory or trusted marketplaces like ThemeForest for lightweight themes.
- Check theme reviews and performance ratings on sites like WPBeginner or ThemeIsle.
- Test your current theme’s impact using tools like Google PageSpeed Insights or GTmetrix. If it’s slowing you down, switch to a lighter alternative.
- Avoid themes with excessive built-in features you don’t need (e.g., sliders or page builders).
- Best Practices:
- Customize your theme minimally to avoid adding heavy plugins or custom code.
- Use a child theme to preserve customizations during updates.
Pro Tip: Run a speed test before and after switching themes to measure improvement. Need help choosing a theme? Contact us for personalized recommendations!
2. Optimize Images for Faster Loading
The Problem: Large, unoptimized images are one of the biggest culprits behind slow WordPress sites. High-resolution images can take seconds to load, especially on mobile devices.
The Solution: Compress and optimize images without sacrificing quality. Use modern image formats like WebP, which offer smaller file sizes than JPEG or PNG.
- How to Implement:
- Install an image optimization plugin like ShortPixel, Imagify, or Smush. These tools automatically compress images upon upload.
- Convert images to WebP format using plugins or tools like CloudConvert.
- Enable lazy loading to defer off-screen images until users scroll to them. Most caching plugins (like WP Rocket) include this feature.
- Resize images to the exact dimensions needed for your site (e.g., 1200px width for full-width images).
- Best Practices:
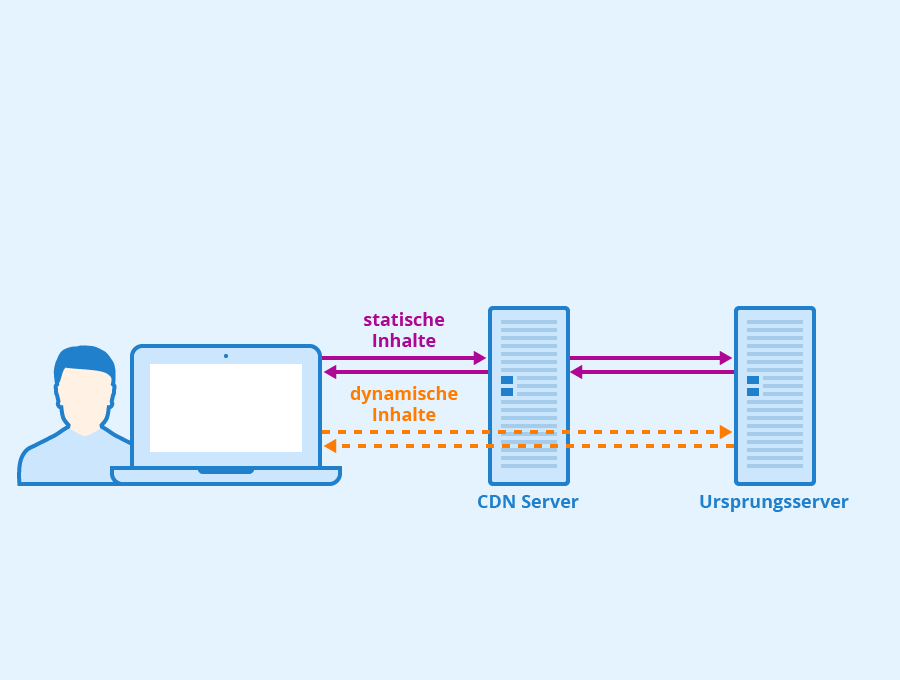
- Use a CDN (Content Delivery Network) like Cloudflare to serve images faster.
- Avoid uploading images directly from your camera; resize them first using tools like Photoshop or Canva.
Pro Tip: Check your image sizes with GTmetrix’s waterfall chart to identify heavy files dragging down your WordPress performance.
3. Use a Reliable Caching Plugin
The Problem: Without caching, WordPress generates pages dynamically for every visitor, taxing your server and slowing down load times.
The Solution: A caching plugin creates static versions of your pages, serving them instantly to users. This reduces server load and significantly improves WordPress load time.
- How to Implement:
- Install a caching plugin like WP Rocket (premium), LiteSpeed Cache (free for LiteSpeed servers), or W3 Total Cache (free).
- Configure the plugin to enable page caching, browser caching, and GZIP compression.
- Set cache expiration times (e.g., 24 hours for static content) to balance freshness and speed.
- Best Practices:
- Clear your cache after making site changes to ensure users see the latest version.
- Use a plugin compatible with your hosting environment (e.g., LiteSpeed Cache for LiteSpeed servers).
Pro Tip: WP Rocket is beginner-friendly and offers advanced features like database optimization. Not sure which plugin suits your site? Let’s talk!
4. Enable a Content Delivery Network (CDN)
The Problem: If your server is located far from your visitors, it takes longer to deliver content, especially for global audiences.
The Solution: A CDN stores your site’s static files (images, CSS, JavaScript) on servers worldwide, serving them from the closest location to each user.
- How to Implement:
- Sign up for a CDN service like Cloudflare, KeyCDN, or StackPath.
- Integrate the CDN with WordPress using a plugin like WP Rocket or CDN Enabler.
- Verify that your CDN is working by checking your site’s source code for CDN URLs.
- Best Practices:
- Use a CDN with a free plan (like Cloudflare) for small sites or blogs.
- Ensure your CDN supports HTTP/3 for faster delivery.
Pro Tip: A CDN can cut load times by up to 50% for international visitors. Test your site’s global performance with Pingdom.
5. Minify CSS, JavaScript, and HTML
The Problem: Unminified files contain unnecessary spaces, comments, and formatting that increase file sizes and slow down rendering.
The Solution: Minification removes these extras, reducing file sizes and speeding up page load times.
- How to Implement:
- Use a plugin like WP Rocket or Autoptimize to minify CSS, JavaScript, and HTML automatically.
- If you’re comfortable with code, manually minify files using tools like UglifyJS (for JavaScript) or CSSNano (for CSS).
- Combine CSS and JavaScript files to reduce HTTP requests (most caching plugins offer this feature).
- Best Practices:
- Test your site after minification to ensure no functionality breaks.
- Exclude critical scripts (e.g., payment gateways) from minification if they cause errors.
Pro Tip: Minification can shave milliseconds off load times, which adds up for mobile users. Run a speed test to see the impact!
6. Optimize Your WordPress Database
The Problem: Over time, your WordPress database accumulates junk like post revisions, spam comments, and transients, slowing down queries.
The Solution: Regularly clean and optimize your database to keep it lean and fast.
- How to Implement:
- Use a plugin like WP-Optimize or Advanced Database Cleaner to remove unnecessary data.
- Schedule automatic cleanups (e.g., weekly) to delete revisions, trashed posts, and expired transients.
- Optimize database tables directly via phpMyAdmin if you’re comfortable with manual tweaks.
- Best Practices:
- Back up your database before optimization to avoid data loss.
- Avoid over-optimizing (e.g., deleting all revisions if you need them for post recovery).
Pro Tip: A clean database can reduce server response time, especially for large sites. Need help with database maintenance? Contact us!
7. Choose a Fast WordPress Hosting Provider
The Problem: Shared hosting or low-quality servers often lack the resources to handle WordPress efficiently, leading to slow load times.
The Solution: Invest in a high-performance hosting provider optimized for WordPress.
- How to Implement:
- Choose managed WordPress hosting from providers like WP Engine, Kinsta, or SiteGround.
- Look for hosts with SSD storage, LiteSpeed servers, and built-in caching.
- Check server locations to ensure they’re close to your audience.
- Best Practices:
- Avoid cheap shared hosting for high-traffic sites.
- Compare hosting plans based on performance metrics, not just price.
Pro Tip: Switching to a faster host can improve WordPress load time by 20-50%. Run a server response test with GTmetrix to evaluate your current host.
8. Reduce External Scripts and Third-Party Requests
The Problem: External scripts (e.g., Google Analytics, social media widgets, or ad networks) create additional HTTP requests, slowing your site.
The Solution: Minimize external scripts and optimize how they load.
- How to Implement:
- Audit third-party scripts using GTmetrix or Chrome DevTools.
- Defer non-critical scripts (e.g., analytics) using plugins like WP Rocket or Async JavaScript.
- Host external scripts locally (e.g., Google Fonts) to reduce DNS lookups.
- Best Practices:
- Remove unused scripts or widgets.
- Use lightweight alternatives (e.g., minimal analytics tools like Fathom instead of Google Analytics).
Pro Tip: Fewer HTTP requests mean faster load times. Test your site’s performance after removing a script to measure the difference.
9. Upgrade to the Latest PHP Version
The Problem: Outdated PHP versions (e.g., 5.6 or 7.0) are slower and less secure, impacting WordPress performance.
The Solution: Update to the latest stable PHP version (e.g., PHP 8.2 or higher) for faster processing and better compatibility.
- How to Implement:
- Check your current PHP version in your hosting control panel or with a plugin like Display PHP Version.
- Contact your hosting provider to upgrade to the latest PHP version.
- Test your site for compatibility issues after upgrading (use a staging site if possible).
- Best Practices:
- Ensure your theme and plugins are compatible with the new PHP version.
- Back up your site before upgrading.
Pro Tip: PHP 8+ can boost performance by up to 30%. Not sure how to upgrade safely? Let’s talk!
10. Limit Post Revisions and Autosaves
The Problem: WordPress saves multiple post revisions and autosaves, bloating your database and slowing queries.
The Solution: Limit or disable revisions to keep your database lean.
- How to Implement:
- Add the following code to your
wp-config.phpfile to limit revisions:define('WP_POST_REVISIONS', 3); // Limits to 3 revisions - Use a plugin like WP-Optimize to delete old revisions.
- Disable autosaves by adding this to
wp-config.php:define('AUTOSAVE_INTERVAL', 300); // Increase autosave interval to 5 minutes
- Add the following code to your
- Best Practices:
- Keep a few revisions for critical pages in case you need to revert changes.
- Schedule regular revision cleanups.
Pro Tip: Reducing revisions can free up database space and speed up queries. Test your database size before and after cleanup.
11. Optimize WordPress Plugins
The Problem: Too many plugins or poorly coded ones can slow your site by adding unnecessary scripts and database queries.
The Solution: Audit and optimize your plugins to ensure only essential ones are active.
- How to Implement:
- Use a plugin like Query Monitor to identify resource-heavy plugins.
- Deactivate and delete unused plugins from your WordPress dashboard.
- Replace heavy plugins with lightweight alternatives (e.g., use Contact Form 7 instead of bulky form builders).
- Best Practices:
- Limit your site to 10-15 essential plugins.
- Regularly update plugins to maintain performance and security.
Pro Tip: A lean plugin setup can cut load times significantly. Need help auditing your plugins? Contact us!
12. Enable Browser Caching
The Problem: Without browser caching, returning visitors must reload your site’s files every time, slowing their experience.
The Solution: Enable browser caching to store static files locally on users’ devices.
- How to Implement:
- Use a caching plugin like WP Rocket or W3 Total Cache to set browser caching rules.
- Add caching headers to your
.htaccessfile for Apache servers:<IfModule mod_expires.c> ExpiresActive On ExpiresByType image/jpg "access plus 1 year" ExpiresByType image/jpeg "access plus 1 year" ExpiresByType image/gif "access plus 1 year" ExpiresByType image/png "access plus 1 year" ExpiresByType text/css "access plus 1 month" ExpiresByType application/javascript "access plus 1 month" </IfModule> - For NGINX servers, ask your hosting provider to configure caching.
- Best Practices:
- Set longer cache times for static files (e.g., images) and shorter times for dynamic content.
- Test caching with tools like Pingdom to ensure it’s working.
Pro Tip: Browser caching can reduce server load and improve WordPress load time for repeat visitors.
Conclusion
Speeding up your WordPress website is critical for delivering a seamless user experience, boosting SEO, and increasing conversions. By understanding what slows down your site and regularly testing its performance, you can pinpoint issues and apply these 12 optimization strategies to fix a slow WordPress site. Start by running a speed test with tools like Google PageSpeed Insights, GTmetrix, or Pingdom to identify your site’s weak points. Then, tackle the low-hanging fruit: optimize images, enable caching, and choose a fast host. For deeper fixes, consider upgrading PHP or auditing plugins. Need help optimizing your WordPress site? Let’s talk to create a tailored plan for your success!
FAQ: Common Questions About WordPress Speed Optimization
What is a good WordPress loading speed?
A good WordPress loading speed is under 2 seconds, with 1-1.5 seconds being ideal. Google recommends a server response time below 200ms and a fully loaded page under 2.5 seconds for optimal user experience.
Does speed affect SEO ranking?
Yes, speed is a direct ranking factor for Google. Faster sites rank higher, as they provide a better user experience. Slow load times can also increase bounce rates, further hurting SEO.
How do I check my WordPress website speed?
Use free tools like Google PageSpeed Insights, GTmetrix, or Pingdom. These provide detailed reports on load times, server response, and optimization opportunities. Test regularly to monitor improvements.
Are free caching plugins enough?
Free caching plugins like W3 Total Cache or LiteSpeed Cache can significantly improve WordPress performance, but premium plugins like WP Rocket offer advanced features (e.g., lazy loading, database optimization) for better results. For small sites, free plugins are often sufficient.